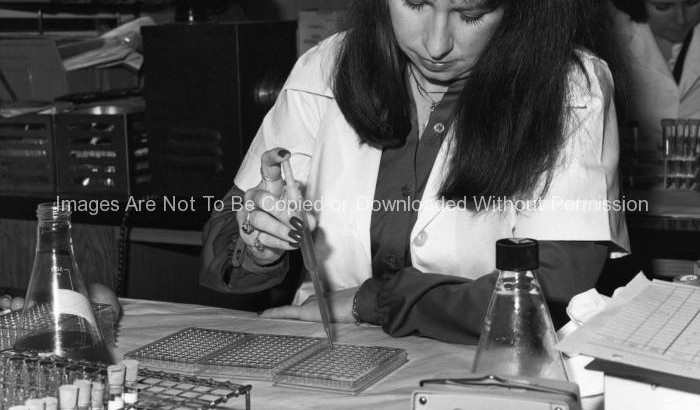
The presence or absence of influenza virus would be determined by using an agglutination test. If it involved the agglutination, or clumping of red blood cells (RBCs), the phenomenon is known as hemoagglutination.
Diagnostic tests available for influenza include viral culture, serology, rapid antigen testing, polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and immunofluorescence assays. Sensitivity and specificity of any test for influenza might vary by the laboratory that performs the test, the type of test used, and the type of specimen tested. Among respiratory specimens for viral isolation or rapid detection, nasopharyngeal specimens are typically more effective than throat swab specimens. As with any diagnostic test, results should be evaluated in the context of other clinical and epidemiologic information available to health-care providers.